What is GEO?
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) is the process of optimizing content for AI-driven platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google SGE. It focuses on semantic clarity, structured data, and contextual alignment to help content get cited or summarized directly in AI-generated responses.
The way people search online is changing fast. Instead of clicking through long lists of links, more people now ask AI tools like ChatGPT for quick answers. Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) is a new way of improving your content so that it appears in answers from AI tools like ChatGPT, Google’s AI Overviews, Gemini, and Perplexity. Instead of focusing only on keywords like traditional SEO, GEO helps content become part of the direct answers these AI engines give.
The term GEO was introduced by researchers at Princeton University in 2023. They defined it as a method to make content more visible in generative search results which is the kind of answers created by large language models (LLMs) instead of regular search engines.
GEO is often seen as the next step after SEO (Search Engine Optimization) and AEO (Answer Engine Optimization). While SEO focuses on ranking in Google and Bing, and AEO helps content show up in answer boxes or voice results, GEO is built for the new world of generative AI, where answers are written by machines and pulled from many sources.
To succeed with GEO, your content needs to be clear, well-structured, and helpful enough to be quoted, cited, or summarized by these AI models.
GEO Benefits in 2025 and Beyond
Searches for information is no longer limited to scrolling through search results. Today, platforms like ChatGPT, Google’s Search Generative Experience (SGE), and Perplexity AI respond with full answers often without linking back to the original websites. This shift means that to stay visible, your content must be structured and relevant enough for these AI systems to directly reference it in their responses.
According to Gartner, traditional search traffic is expected to drop by 25% by 2026, as AI-generated summaries increasingly replace standard search results. A 2025 McKinsey report found that 65% of businesses are actively using generative AI, nearly doubling from the year before. At the same time, public trust in AI-generated content continues to grow: studies show that around 70% of users already trust AI answers as much as traditional search results.
These shifts have created a new challenge: the rise of the AI dark funnel. This is the part of the customer journey that happens entirely inside AI tools, when users ask a question, compare products, or research solutions, all without visiting a website. Combined with the rise in zero-click searches, where answers are shown instantly without the user clicking a result, visibility through old-school SEO is no longer enough.
That’s where GEO (Generative Engine Optimization) comes in. GEO helps your content become part of the answers that AI generates. It focuses on clarity, structure, and trust-building signals, aligning closely with Google’s E-E-A-T guidelines: Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trust.
How Generative Engines Work (AI Search Mechanics)
When you ask a tool like ChatGPT or Google’s AI Overview a question, it does not just scan web pages like Google Search used to. Instead, it uses a type of artificial intelligence called a large language model (LLM) to understand your question, find the right information, and write a full response in natural language.
Here’s a simple look at how that process works:
1. The Engine’s Brain: Transformers and Embeddings
LLMs are built on transformers, which are advanced models trained to understand patterns in human language. These models don’t look for exact keyword matches. Instead, they use something called embeddings, which turn words and phrases into numbers that represent their meaning.
This helps the AI find not just matching words, but content that means the same thing, even if it’s written differently. That’s why well-written, clear content with natural language performs better in generative answers.
2. Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)
Many modern AI engines use a method called RAG, or retrieval-augmented generation. This means the AI doesn’t just guess the answer from memory. Instead, it pulls in real content from trusted sources to make its response more accurate.
To do this, the AI scans a database of indexed content, finds the most relevant pieces, and uses them to build a custom answer. Your content can only be part of that if it is easy to find, clearly structured, and contains real value.
3. Chunking: How AI Reads in Pieces
AI engines often don’t read your entire web page at once. They break it into chunks, small sections of text, usually between 200 to 400 words. These chunks are processed one at a time.
If a chunk includes clear answers, facts, or headings, it is more likely to be used in a response. That’s why writing in short sections with meaningful headers is so important.
4. Source Prioritization: What Makes AI Trust You
AI models are trained to give helpful and accurate answers. To do this, they tend to prefer:
- Authoritative websites
- Pages with clear structure
- Sources that other websites mention or link to
- Content that matches user intent and is easy to understand
If your site has strong internal structure, external mentions, and uses precise language, it increases your chances of being selected.
5. Formatting That Helps You Get Picked
How you format content plays a big role. AI engines like:
- Headings that clearly show what each section is about
- Bullet points and numbered lists
- Short paragraphs
- Tables with clean data
- Schema markup (like FAQPage or Article)
These formats make your content easier for AI to scan, understand, and reuse in its answers.
Before you continue:
If you want a step-by-step checklist to optimize your content for SEO, AEO, and GEO, download our free GEO Content Optimization Checklist → instantly available via Google Docs.
Core Components of GEO
Once you understand how generative engines function, the next step is knowing how to prepare your content to be chosen, cited, and synthesized by these AI systems. Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) is more than content writing, it’s about structuring and shaping your content to match how AI retrieves and evaluates information.
This section outlines the foundational building blocks of a strong GEO strategy.
1. Entity Clarity
Entity-based optimization is at the heart of GEO. Entities like people, places, things, and concepts are how AI systems interpret meaning. Your content must clearly define and consistently refer to entities using precise language.
- Use proper nouns and exact terms (e.g., “Google Search Generative Experience” instead of “Google’s AI tool”).
- Reinforce entity context by connecting it to known facts (e.g., “ChatGPT, developed by OpenAI, is…”).
- Include internal links to supporting content and external links to trusted references.
This clarity allows AI to confidently include your content when building responses involving those entities.
2. Contextual Chunking
Generative engines don’t always read an entire page. They break content into 200–400 word “chunks” that they can easily evaluate. Each chunk should stand on its own with a clear heading and complete context.
Best practices:
- Use short paragraphs (2–4 lines)
- Add headers every 2–3 paragraphs
- Start each section with a strong, clear sentence that defines the topic
Chunking improves AI readability and increases the chances that a specific portion of your content is selected.
3. Structured Data & Schema Markup
Schema markup helps AI engines understand the structure and purpose of your content. It also increases the likelihood of appearing in enhanced results like AI summaries or answer panels.
Examples:
- FAQPage schema for question-based content
- Article schema with author, datePublished, and headline
- Product schema with name, offers, and review
Structured data clarifies relationships between parts of your content and enhances machine understanding.
4. Semantic Embeddings
Unlike keyword matching in SEO, GEO focuses on how AI understands semantic meaning through embeddings of numerical representations of words and concepts. Writing that uses semantically rich, natural language increases relevance.
Tips:
- Use synonyms and contextually related terms
- Avoid keyword stuffing; instead, write conversationally
- Answer questions fully using varied but clear vocabulary
Content aligned with semantic patterns is more likely to appear in generative responses.
5. Natural Language Alignment
AI engines are trained on human-like language. GEO content should mimic this:
- Write in a tone that feels natural and informative
- Use question-and-answer formats where appropriate
- Use active voice and plain English for clarity
This increases the likelihood that your content will blend naturally into AI-generated text.
6. AI Engine Differentiation
Different AI engines interpret content differently. What works for ChatGPT might not be prioritized by Perplexity or Google Gemini.
Key distinctions:
- ChatGPT: Favors clean, sourced answers and context-rich responses
- Gemini (Google SGE): Draws from web sources; prioritizes schema, structured content, and factual relevance
- Perplexity: Extracts concise answers; emphasizes source citation and technical depth
Tailor your content for each engine by auditing how they cite, summarize, and prioritize information.
Together, these components help your content do more than rank but they ensure it is understood, trusted, and used by generative engines across platforms. GEO transforms your pages into structured, intelligent content systems that AI wants to cite.
GEO vs SEO vs AEO – What’s the Real Difference?
In 2025, the way people search has fundamentally changed. Instead of typing keywords into a search bar and clicking through results, users now speak naturally, ask full questions, and receive complete answers from AI systems like ChatGPT, Google’s Search Generative Experience (SGE), and Perplexity AI. These platforms no longer just list websites. They summarize and generate answers directly.
To stay visible in this environment, content needs more than just keywords or backlinks. It must be structured, cited, and contextually rich enough to be understood and quoted by generative engines. This is where GEO (Generative Engine Optimization) becomes critical. It builds on what SEO and AEO started and prepares content for how modern AI systems actually retrieve and present information.
Let’s break down how these three strategies differ and where they connect.
SEO: Ranking in Traditional Search
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is the classic method. It helps your content appear in Google or Bing when users search using specific keywords. SEO focuses on optimizing metadata, building links, and ensuring pages are fast, crawlable, and mobile-friendly.
- Goal: Appear in organic search results
- Strength: Drives link-based traffic
- Limitation: Loses effectiveness in zero-click searches
AEO: Winning the Answer Box
Answer Engine Optimization (AEO) focuses on optimizing for platforms that display direct answers, such as Google’s featured snippets or voice search. It prioritizes clarity and structure to increase the chances of being selected as an instant answer.
- Goal: Provide quick, credible answers to user questions
- Focus: Structured data, schema markup, scannable formats
- Limitation: Still relies on traditional search engine frameworks
GEO: Being Chosen by AI
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) targets large language models like ChatGPT, Claude, Gemini, and Perplexity. These AI engines don’t display links. Instead, they synthesize multiple sources to generate conversational answers. GEO helps your content get cited, paraphrased, or directly used in those responses.
- Goal: Be referenced within AI-generated answers
- Focus: Semantic clarity, entity-level precision, source citation
Strength: Increases AI-based visibility where no link is shown
The Core Differences of SEO, AEO and GEO
|
Factor
|
SEO
|
AEO
|
GEO
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
Query Type
|
Short-tail keywords
|
Direct, question-based
|
Conversational, context-rich prompts
|
|
Target Platform
|
Search engines (Google, Bing)
|
Voice assistants, SERP features
|
Generative engines (ChatGPT, SGE, Perplexity)
|
|
Result Format
|
Link list (SERP)
|
Featured snippet, answer box
|
Synthesized response with citations
|
|
Optimization Goal
|
Rank a webpage
|
Appear as the instant answer
|
Be cited in AI-generated content
|
|
Format Focus
|
Meta tags, content depth, backlinks
|
Schema, structured data
|
Chunking, clarity, semantic structure
|
|
Measurement Metrics
|
CTR, organic rankings
|
Featured snippet wins, voice mentions
|
AI citation share, generative appearance score
|
Why GEO Complements SEO and AEO
GEO does not replace SEO or AEO. It builds on both. The fundamentals of SEO, like crawlability and quality content, remain important. AEO teaches us the value of formatting for quick comprehension. GEO pushes this further by optimizing content for how AI reads, understands, and decides what to include in its answers.
It adds new requirements like:
- Clear, extractable content blocks
- Entity-level precision and fact alignment
- Reliable citations and external credibility
- Structured layouts that help LLMs process context
Together, SEO, AEO, and GEO form a unified strategy that aligns your content with human behavior and machine logic.
Why You Need All Three: The Modern Funnel
The modern funnel now requires integrating SEO, AEO, GEO, and even channels like Pay-Per-Click Advertising to capture intent at every stage.
|
Use SEO to
|
Use AEO
|
Use GEO to
|
|---|---|---|
|
Help Google crawl and rank your content
|
Get picked for featured snippets
|
Be referenced and quoted in AI-generated answers
|
|
Improve visibility for high-volume search terms
|
Appear for FAQ-style, voice, and quick queries
|
Influence long, conversational prompts in AI tools
|
|
Build trust through E-E-A-T and backlinks
|
Answer direct questions clearly
|
Become the go-to source for AI summarization
|
Key GEO Ranking Signals & Metrics
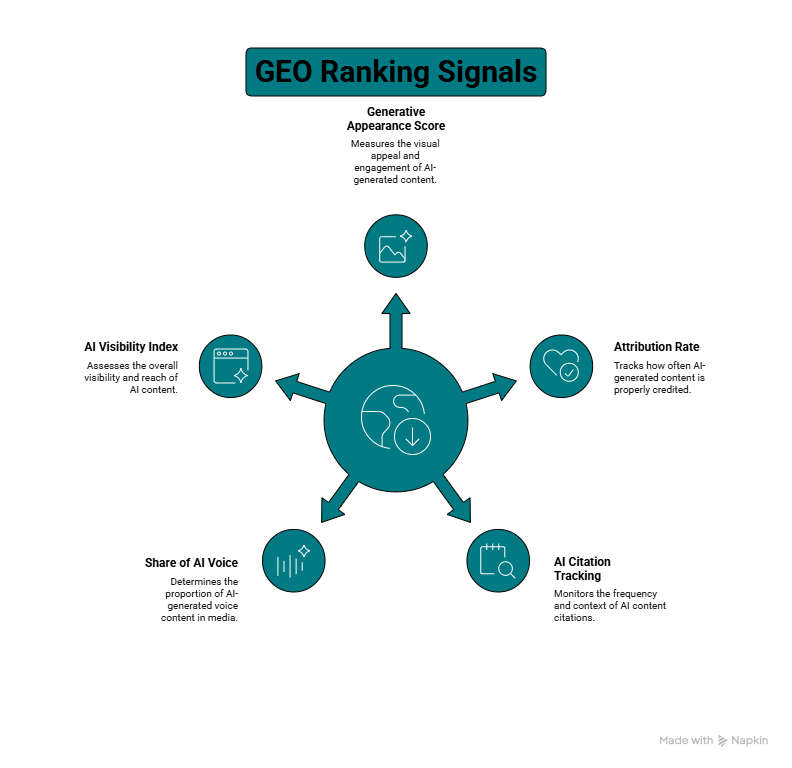
In this new AI-first ecosystem, brands need to track how their content performs within generative engines like ChatGPT, Google’s AI Overviews, Perplexity, Claude, and others. This requires new performance metrics tailored to how AI selects, summarizes, and cites content.
Below are the emerging GEO-specific KPIs you should measure in 2025 and beyond:
1. Generative Appearance Score (GAS)
This measures how often your content is included in AI-generated answers across various queries. Instead of simply tracking page impressions in Google Search Console, this metric captures whether your brand is referenced or included in generative results.
- Example Insight: If you appear in Perplexity AI’s summaries for 10 out of 50 tracked queries, your GAS is 20%.
- How to Monitor: Use tools like Brand GPT Trackers or manually prompt LLMs with key queries.
2. Attribution Rate
When an AI tool cites a source, it might show the name of the domain or link to it directly. Your Attribution Rate measures how often your content is not only used but credited visibly in the output.
- Why It Matters: Visibility without attribution means zero clicks, traffic, or recognition.
- What to Watch: Presence of your domain name or brand in tooltips, footnotes, or response citations.
3. AI Citation Tracking
This is similar to backlink tracking but applied to generative engines. You’re not tracking external hyperlinks, you’re analyzing whether your content is being cited as a source by AI models in their responses.
- Tools: Brand GPT dashboards, prompt-based citation audits, and tools like SISTRIX’s AI Visibility tools.
- Impact: Frequent citations increase brand authority in AI systems, improving future inclusion likelihood.
4. Share of AI Voice
This metric captures how often your brand appears compared to competitors across a defined set of prompts.
- Think of it like Share of SERP in traditional SEO but now focused on voice in AI-generated narratives.
- Example: If your brand appears in 30% of generative responses for industry prompts, your Share of AI Voice is 30%.
- How to Use: Track competitors across prompts and model types (e.g., Gemini vs. ChatGPT).
5. AI Visibility Index
A blended index combining GAS, Attribution Rate, and Citation Frequency into one visibility score. This helps measure your overall footprint inside AI-generated content environments.
- Use Cases:
- Benchmark against industry norms
- Report performance to stakeholders
Track longitudinal visibility in LLMs
Case Study: Chat GPT Picks the Underdog
Context: One of our client, a small SaaS startup in the project management space was struggling to outrank dominant competitors like Monday.com or Trello in traditional SERPs.
What We Did:
We focused on GEO principles: clearly chunked product comparisons, structured schema (FAQ & Product), and cited data from third-party reviews.
Result:
When users asked “Best project management tool for freelancers?” on Perplexity, their content was cited in the top paragraph not because they ranked #1 on Google, but because their chunk was clean, sourced, and directly answered the prompt.
Takeaway:
For small businesses it is not enough to rank on Google with SEO but they need visibility in the places where real decisions happen. GEO pushes them into the conversation by getting cited inside GPT, Perplexity, Gemini, and other generative engines.
Future of GEO: Multimodal, Voice, and Proactive AI
Generative engines are changing how users interact with information—and the next phase goes beyond text-only search.
Multimodal and voice interaction
AI tools are now capable of processing text, images, video, and voice. Google’s Gemini, for example, supports multimodal prompts where users can submit an image or voice message and receive a dynamic answer. This means that content creators must think beyond written text and design content that is understandable across formats.
To future-proof your visibility:
- Add meaningful visuals with descriptive alt-text
- Use semantic annotations to describe media assets
- Provide transcripts or summaries for videos and audio files
Voice-first interfaces, like those used in smart assistants, require content that’s structured in short, clear, and direct segments—almost like scriptwriting.
Hyper-personalization
AI systems are increasingly tuned to serve answers based on user location, intent, browsing patterns, and more. This trend means content must not only be relevant but adaptable.
You can prepare by:
- Tagging your content with clear metadata about the topic, audience, and context
- Structuring articles in modular sections that can be reused in personalized responses
- Creating variations of content for different user intents
Continuous retraining and optimization
Unlike traditional SEO, GEO is not a one-time optimization. AI systems update frequently, pulling from new sources and refining how they interpret intent and trust.
To stay current:
- Regularly update outdated content
- Monitor how your content performs across AI tools like ChatGPT, Gemini, and Perplexity
- Track inclusion patterns and citation frequency using AI visibility dashboards
Final Thought about GEO: Don’t Just Rank, Be the Answer
You’ve probably optimized for Google. You’ve probably written for humans. But now, the search box is disappearing and answers are being built before users even visit your site.
Not long ago, success meant showing up on page one. Today, it means showing up inside the answer.
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) is the shift from link-based visibility to AI-first credibility.
Generative engines don’t just list what exists, they decide what is important to show. They quote what’s clear, cite what’s credible, and summarize what’s structured. In that world, your content has a choice: be an overlooked page, or be the chosen source.
Only the brands that adapt now will get trusted, reused, and remembered.
If your voice isn’t training the machine, someone else’s is.
Start optimizing for generative engines and don’t just rank. Be the answer.
Ready to Future-Proof Your Content for AI Search?
How is GEO different from traditional SEO?
Do I need GEO if I already do SEO and AEO?
How do I know if GEO is working for my site?
What kind of content is best for GEO?
Ermus is an SEO specialist and content writer with 2 years of experience in driving website growth through effective search strategies and engaging content. Specializing in local SEO, on-page/off-page optimization, and semantic content, she applies Koray Tuğberk GÜBÜR’s holistic SEO methods to build authority and relevance across topics. Ermus stays ahead of the curve, constantly refining strategies to adapt to evolving search trends.